1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
|
# confirm
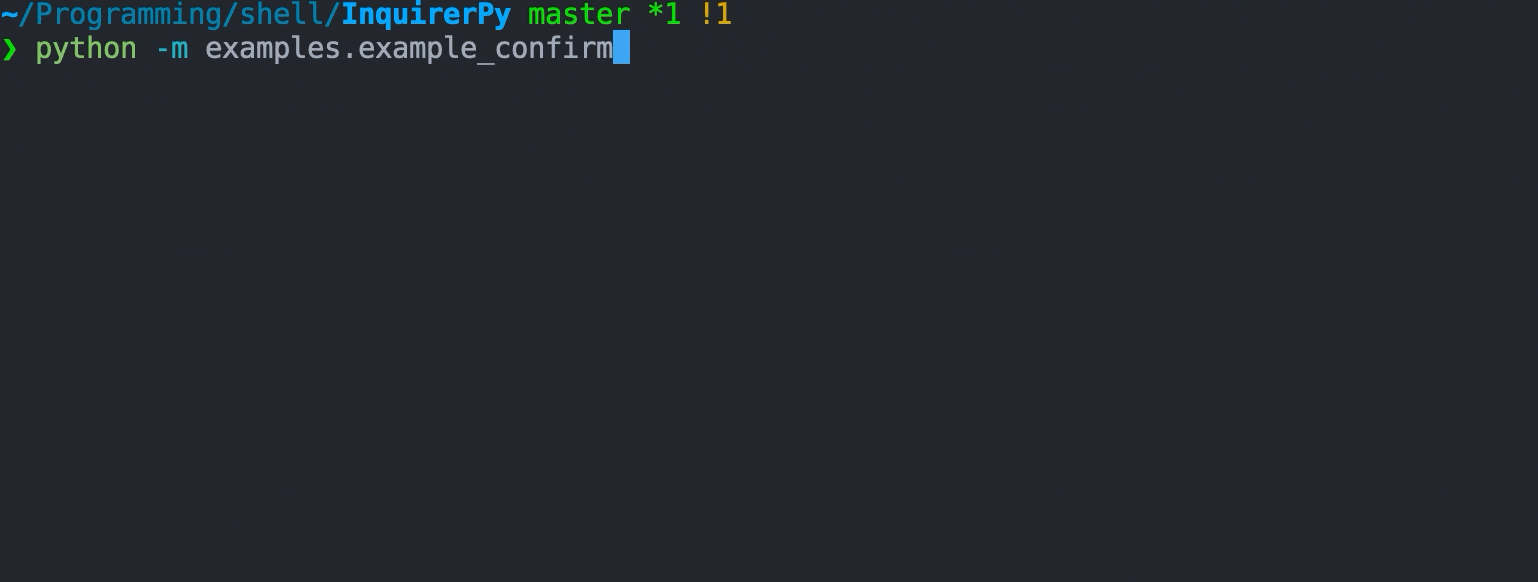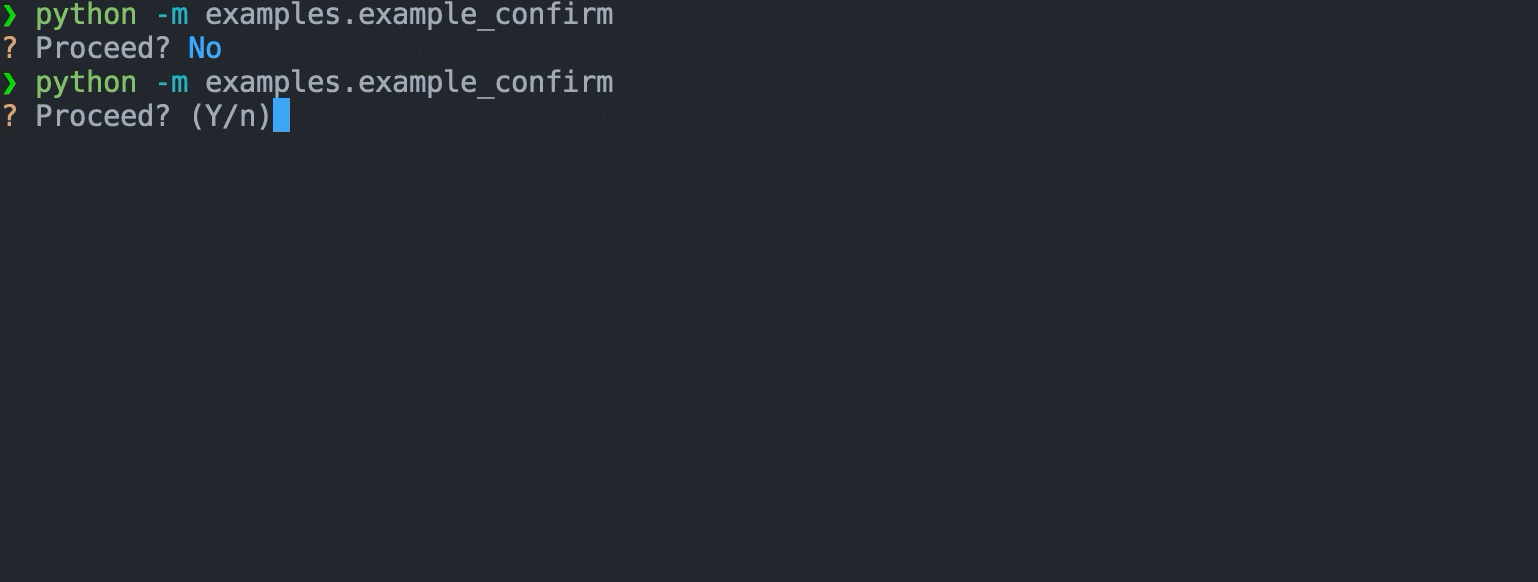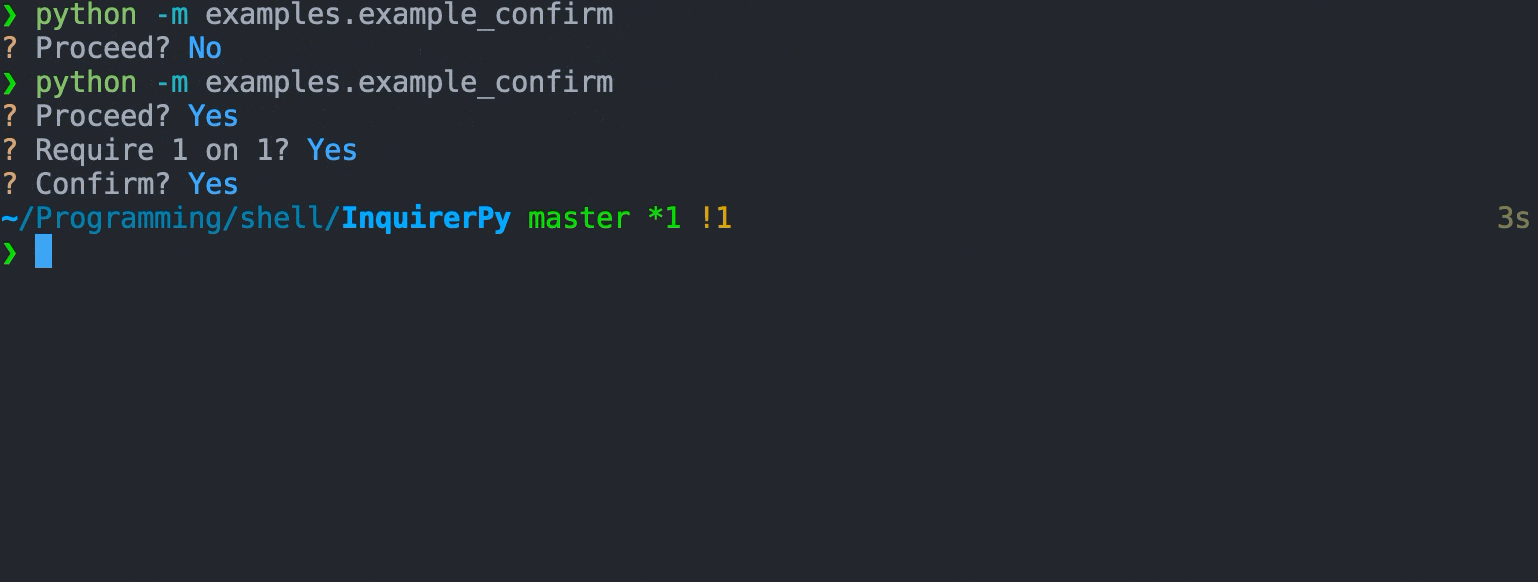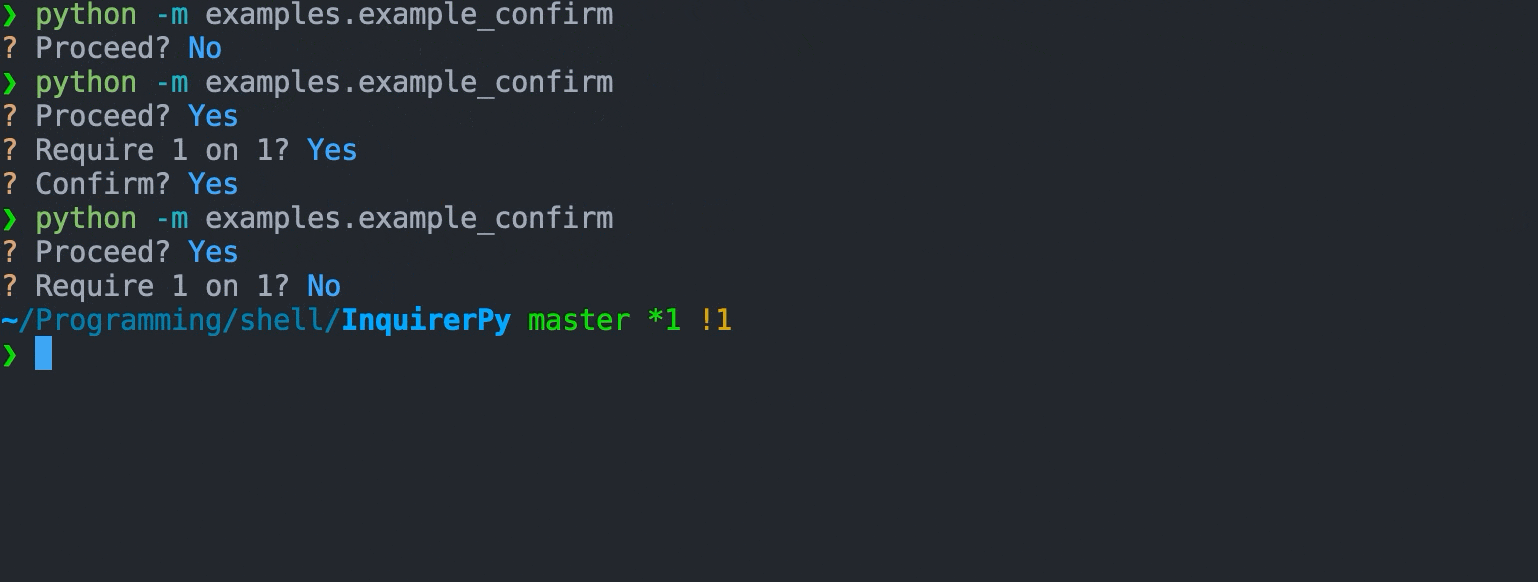
A prompt that provides 2 options (confirm/deny) and can be controlled via single keypress.
## Example
<details>
<summary>Classic Syntax (PyInquirer)</summary>
```{eval-rst}
.. literalinclude :: ../../../examples/classic/confirm.py
:language: python
```
</details>
<details open>
<summary>Alternate Syntax</summary>
```{eval-rst}
.. literalinclude :: ../../../examples/alternate/confirm.py
:language: python
```
</details>
## Keybindings
```{seealso}
{ref}`pages/kb:Keybindings`
```
```{include} ../kb.md
:start-after: <!-- start kb -->
:end-before: <!-- end kb -->
```
Besides the default keybindings, keybindings will be created for the parameter `confirm_letter` and `reject_letter` which
by default are `y` and `n` respectively.
Pressing `y` will answer the prompt with the value True and `n` will answer the prompt with the value False.
```
{
"confirm": [{"key": "y"}, {"key": "Y"}], # confirm the prompt
"reject": [{"key": "n"}, {"key": "N"}], # reject the prompt
}
```
## Using Different Letters For Confirm/Deny
```{tip}
You can also change the letter by using the `keybindings` parameter and change the value for "confirm" and "reject" key.
```
In certain scenarios using `Y/y` for "yes" and `N/n` for "no" may not
be appropriate (e.g. multilingual).
You can change this behavior by customising the following parameters:
- `confirm_letter`
- `reject_letter`
- `transformer`
```{hint}
Changing the `transformer` is also necessary as the default behavior will print `Yes` for `True`
value and `No` for `False` value.
```
```{note}
This have effects on keybindings, new keybindings will be created based on the value of `confirm_letter` and `reject_letter`
to answer the question with True/False.
```
<details>
<summary>Classic Syntax (PyInquirer)</summary>
```{code-block} python
from InquirerPy import prompt
questions = [
{
"type": "confirm",
"default": True,
"message": "Proceed?",
"confirm_letter": "s",
"reject_letter": "n",
"transformer": lambda result: "SIm" if result else "Não",
}
]
result = prompt(questions=questions)
```
</details>
<details open>
<summary>Alternate Syntax</summary>
```{code-block} python
from InquirerPy import inquirer
inquirer.confirm(
message="Proceed?",
default=True,
confirm_letter="s",
reject_letter="n",
transformer=lambda result: "SIm" if result else "Não",
).execute()
```
</details>
## Default Value
The parameter `default` controls 2 behaviors for the prompt.
It affects how the instruction is displayed, whether the `confirm_letter` is capitalised or `reject_letter` is capitalised.
It affects what value to be returned when user directly hit the key `enter` instead of the `confirm_letter` or `reject_letter`.
By default, since `default` value is `False`, the `reject_letter` is capitalised.
```
? Proceed? (y/N)
```
If `default` is `True`, the `confirm_letter` is capitalised.
```
? Proceed? (Y/n)
```
## Reference
```{eval-rst}
.. autoclass:: InquirerPy.prompts.confirm.ConfirmPrompt
:noindex:
```
|